You're here:
How to Start an Online Business in 2025

Want to start your dream business online? An online business has many advantages over the traditional brick-and-mortar. You don't have to pay certain taxes, rent, or other expenses. Plus, you can build an appealing website for less than $100 a month.
But running an online business is challenging, and many startups fail in their first year. Before you start, think carefully about the pros and cons. You also need a plan – which is where we come in!
We've created a step-by-step guide to help you turn your online business idea into a reality.
The 10 steps to starting an online business are:
- Choose your niche
- Decide on a business model
- Analyze your finances
- Formalize a business plan
- Ensure business registration and compliance
- Build your website
- Develop a marketing plan
- Establish payment processes
- Launch your business
- Get ready for taxes
Let’s get started!
1. Choose your niche
Your first step is to choose your business niche. To generate some ideas, ask yourself questions like:
- What am I passionate about?
- What am I knowledgeable about?
- What are my skills?
Come up with a shortlist of three to five niches. Then, conduct a market analysis for each one.
Here are some things to research:
- The problems and needs of your target market
- Market demand for a product or service
- The competitive landscape: Who’s already out there?
- Average sale prices or commission fees
- Keywords your potential customers use to find products or services
Choose a niche that’s not too competitive and that offers a healthy potential profit margin. Make sure it’s something you enjoy too. Hopefully you’ll be doing it for at least a few years!
If you want to further explore digital opportunities, check out how to build your own business in the creator economy.
2. Decide on a business model
Once you’ve chosen your niche, you need to decide on a business model. There are lots of online business types, such as eCommerce, dropshipping, and affiliate marketing. Each method has pros and cons, so which is the most suitable depends on your preferences.
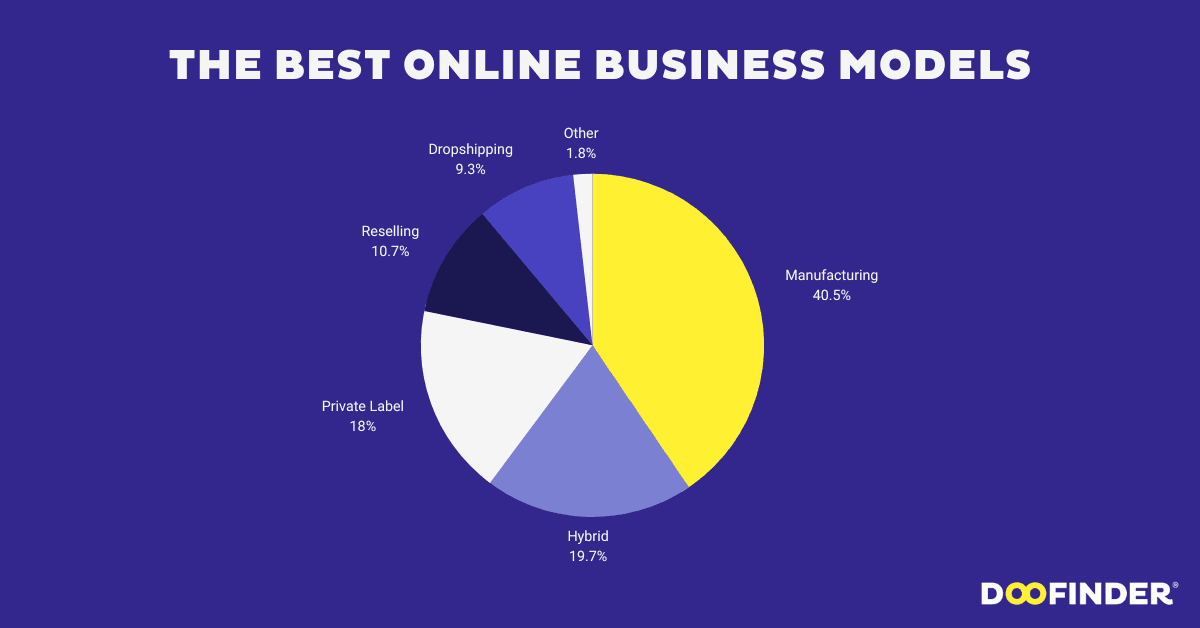 Data sourced from Doofinder
Data sourced from Doofinder
To help you decide, we've outlined three common business models and their pros and cons:
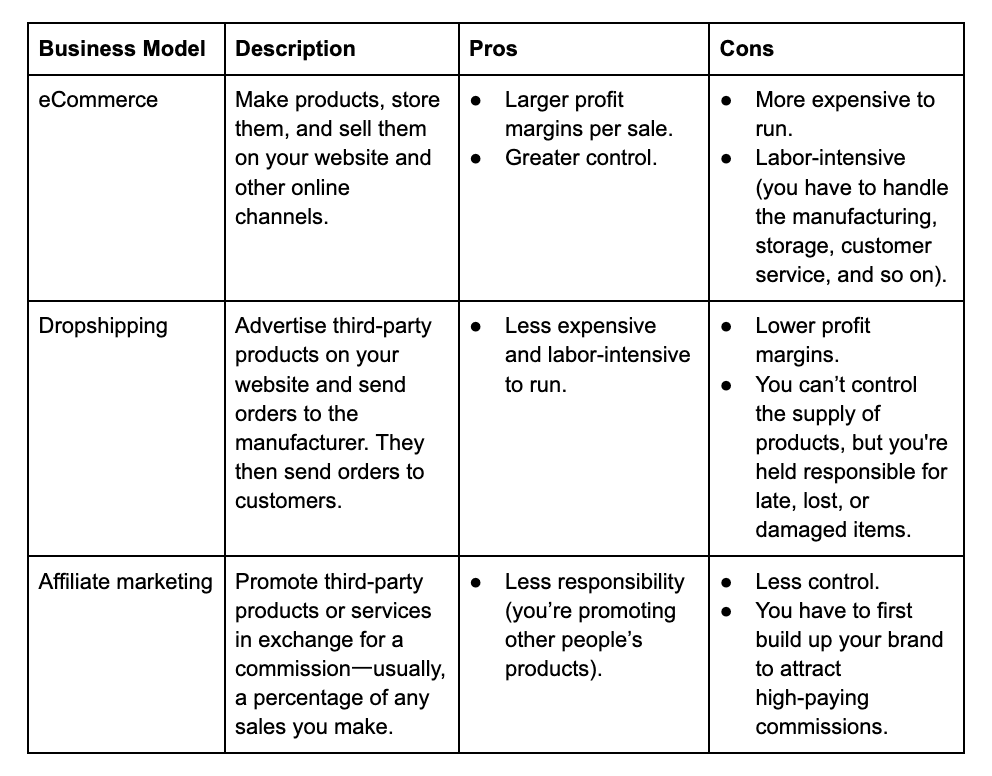
3. Analyze your finances
Next, you need to analyze your finances to determine how much you have to spend. There are many startup costs to consider, including:
- Raw materials and/or stock
- A website
- Software and equipment
- Rent for warehouse space
- Advertising and marketing
Look at your monthly income and expenses, whether that’s through a balance sheet or your cash flow planning. How much do you have left each month? What savings do you have? Based on your figures, you can set a realistic budget for your business. You may need to apply for a small business loan or grant to get started.
Once you’re up and running, it’s important to stay on top of finances to make sure your dream business doesn't sink. One solution is to invest in software for small business owners, potentially a cloud ERP. This software pulls data from across your business to help you identify areas for improvement and pinpoint cost-saving opportunities, all while growing your venture.
This software also offers a range of features to help you manage your budget, track income and expenditure, and more—information that’s vital for setting future budgets and ensuring sustainable growth.
You can also check out financial tips for online creators to help manage your online business finances effectively.
4. Formalize a business plan
A business plan provides a roadmap to launch your business successfully and operate smoothly. It should include the following information:
- A company overview (niche and business model)
- Your goals and objectives
- Market opportunities
- Your target audience
- Competitors
- Product or service offerings
- Value proposition (how your product or service solves your target audience’s problem)
- Budget and estimated costs
- Marketing channels (such as social media or email)
- A timeline and key milestones
- Key performance indicators (KPIs), such as sales, new customers, or revenue
- Your exit strategy
This is a great foundation. If you already have eyes to growth after launch, learn more about business scaling strategy or how to grow your freelance business.
If your business plan involves online courses, consider learning how to set up a successful sales funnel to turn your audience into paying customers.
5. Ensure business registration and compliance
You also need to name your business and register it as a sole proprietorship, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation. It’s free to set up a sole proprietorship, but an LLC or corporation is safer from a legal perspective. That’s because they limit your personal liability in case of lawsuits and also offer tax savings. Since you can choose which state you want to register your business in, learn about the best states to form an LLC.
You’ll need to apply for a business license (such as an EIN number) and get any relevant permits, such as seller’s permits. You might also need to go ahead and register for sales tax, VAT or GST!
Finally, make sure you follow any relevant online regulations. For example, if you want to operate in the EU or UK, you must follow the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This determines how you can collect and process customer data.
If you have any questions, it’s worth speaking to an attorney or contacting your local Small Business Administration (SBA) office for advice.
6. Build your website
To do this, you first need to buy and register a domain name with a domain registrar like GoDaddy or NameCheap. Your domain name is usually your business name with a .com extension, but there’s a range of domain extensions available (some more expensive than others). You can also get a domain name from your hosting provider. Keep in mind you can buy a domain name anonymously rather than having your personal details directly linked to it in the public directory. This is something many site owners choose to do, so check if this is an option when picking a hosting provider. Your hosting provider stores your website on a server, either with other websites (shared hosting) or on its own (dedicated hosting). Shared hosting is cheaper, but dedicated hosting offers better security and faster loading. So, research which option is best for your needs.
If you’re going to build the website yourself, your next step is to choose a content management system (CMS). Popular CMS platforms include WordPress, Wix, Squarespace, and Joomla.
Market value of popular content management systems
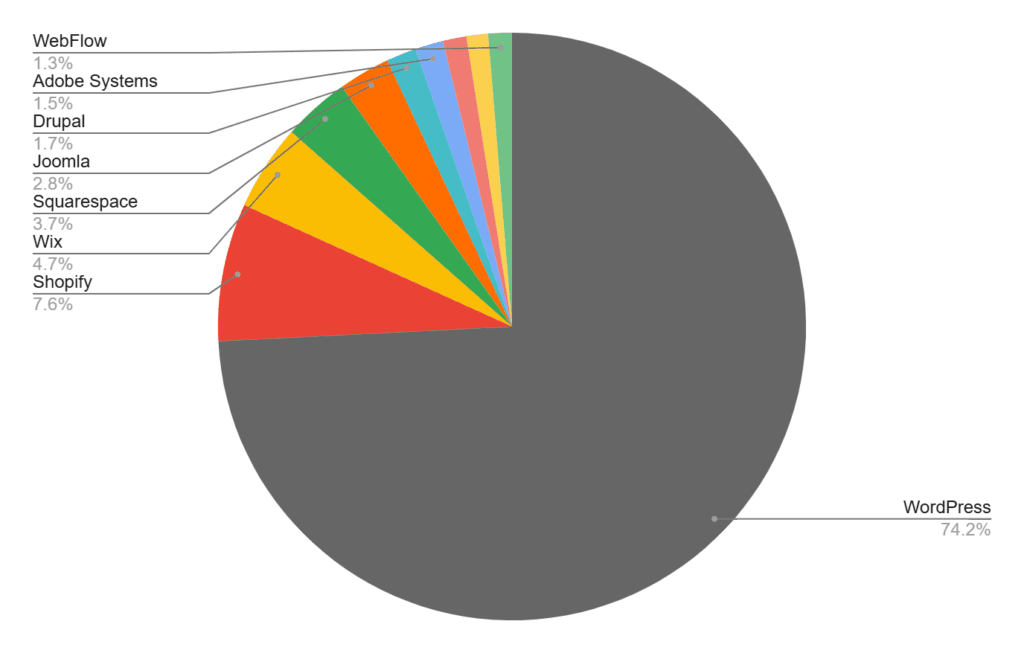 Data sourced from codexpert.io
Data sourced from codexpert.io
With a CMS platform, you can create website pages and content without coding. Many online business owners prefer WordPress, but compare different options by looking at:
- Ease of use
- Features
- Customization options
- Themes and plugins
- Security
- Pricing
Before diving into your website design and structure, create a unique and memorable logo for your online business. This symbolic image not only reflects your brand's core values, but also shapes the overall visual direction of your website. Strive for a simple yet striking design, and choose colors and fonts that mirror your brand's personality.
Once you’ve chosen your platform, choose a theme and customize your site for the type of business you’re starting. For instance, for an eCommerce store, you’ll want a plugin like WooCommerce or Shopify.
It’s best to keep your website simple at this stage, but you’ll want the following regardless:
- A homepage
- An “About Us” page
- A “Contact Us” page
- A page to showcase your products (if applicable)
- A checkout page
- A sign-up form for your mailing list
- An area for customer reviews
- A blog
A blog is a great way to provide more value to your customers, keeping them on your site for longer and building customer loyalty post-sale. It also helps you rank better on search engines, which is essential if you want customers to find your website.
Finally, optimize your website for search engines with SEO (search engine optimization). Here are some ways to optimize your site:
- Use two to three relevant keywords on each page
- Ensure your site loads quickly
- Make sure your site is easy to navigate
- Use a responsive design to make your site mobile-friendly
- Write high-quality blog content
7. Develop a marketing plan
Your next step is to develop a relevant marketing plan. There are many marketing strategies to choose from, including:
• Content marketing. Content like blog posts, videos, and infographics is great for promoting your business. Paired with SEO, it provides free search traffic to your website. • Social media marketing. Since most people are on social networking sites, it’s vital to develop a presence on at least one platform. This way, you can build brand awareness and engage with potential customers. • Email marketing. Send email newsletters, exclusive discounts, and so on to keep customers engaged and reward their loyalty. • Paid advertising. You can also pay to advertise on social media platforms and search engines like Google.
For extra tips, check out these 5 best practices for marketing to international customers online. These tips also apply to buyers in your hometown!
Ultimately, there’s some trial and error involved here. Try a mixture of marketing strategies, and see which gets the best results.
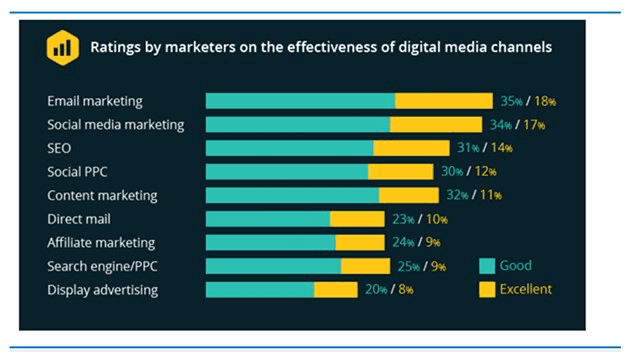 Image sourced from mediaforce
Image sourced from mediaforce
8. Establish payment processes
If you’re selling products in your online store, decide how to accept customer payments. Most websites offer several options, such as credit/debit cards, PayPal or Stripe.
You could also consider Apple Pay or Google Pay, which一when paired with a plugin like Shopify一offer an accelerated checkout option. This lets customers buy an item with a single click instead of going through the whole checkout process.
If you need more guidance, check out how to choose a payment gateway for your business.
Whichever method you choose, set up a payment schedule to get paid daily, weekly, or monthly depending on your preference. Decide if you want one-off or recurring payments.
9. Launch your business
Before you go live with your site, it’s important to market your business in the weeks or months beforehand. This way, you can build anticipation and ensure a successful launch.
Try adding a “countdown to launch” timer on your homepage, with a sign-up form to start building your mailing list. Also, get on your target audience’s preferred social media sites to build hype. You can also connect with popular influencers in your niche to raise awareness.
When you’re ready to launch, announce this on all your channels. You could then have a virtual or in-person launch party and offer discounts or freebies to tempt customers to your site.
10. Get ready for taxes!
As the sales start rolling in, you need to stay aware of the sales tax policies wherever you – and your customers – are located. Ecommerce tax laws, and other policies targeting online sales, are increasingly common around the world.
So, you might be liable for tax obligations from your very first sale, as is often the case with EU VAT, or you might be able to wait awhile until you hit $100,000 in sales in a US state. The US sales tax rules vary a lot depending on the jurisdiction.
To learn more about internet tax laws or online sales tax obligations, head to the sales tax guide for online businesses. It’s complicated! But luckily, software like Quaderno helps you automate the tax compliance process – so you can focus on growing the business you love.
You can also learn about other tax planning tips for small businesses to help you streamline processes from the get-go.
Takeaway
Online businesses offer several advantages over brick-and-mortar stores, especially in today’s economy. Starting an online business is now easier than ever, and you don’t need previous experience to do it.
The key is to use whatever tools are available to you, and there are loads of them online! ERP systems, tax compliance software, payment gateways, email marketing automation – all of these are designed to help you build the best online business and grow with confidence.
Note: At Quaderno we love providing helpful information and best practices about taxes, but we are not certified tax advisors. For further help, or if you are ever in doubt, please consult a professional tax advisor or the tax authorities.